Describe How Compounds Use Their Valence Electrons to Form Bonds
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share valence. They are formed when electrons are shared between two atoms.

In This Inquiry Activity Students Use Beads As Valence Electrons To Discover And Visualize How Atoms Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Activities Covalent Bonding
Energy is always released when bonds are made.

. This forms a type of covalent bond called a single covalent bond. To form ionic bonds Carbon molecules must either gain or lose 4 electrons. The atoms will join covalently with other atoms to gain more stability which is achieved by forming a complete electronic shell.
Chemical bonds are the attractive forces that hold atoms together in the form of compounds. An ionic bond where. The number of valence electrons determines what other atoms an atom can bond with and how many.
In valence bond theory. Each bonding atom can also. Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules.
The valence electrons are part of most of the chemical reactions because they contain more. An ionic bond is formed when one atom accepts or donates one or more of its valence electrons to another atom. The other possible way that valence electrons can be involved in bonding is by being shared by two atoms in order to complete the Rule of Octet in a Molecular covalent Bond.
The chemical bond formed between 2 atoms through the mutual sharing of one or more valence electrons between non-metallic elements is called a covalent bond. The loss or gain of valence electrons allows ions to obey the octet rule. Atoms form chemical bonds to make their outer electron shells more stable.
Chemical bonds are the attractive forces that hold atoms together in the form of compounds. Well valence electrons can form covalent or ionic bonds. This idea forms the basis for a quantum mechanical theory called valence bond VB theory.
In essence any covalent bond results from the overlap of atomic orbitals. Therefore carbon molecules share their 4 valence electrons through. This is highly unfavorable.
In this model bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two atomic orbitals on different atoms each. By sharing their outer most valence electrons atoms can fill up their outer electron shell and gain stability. The type of chemical bond maximizes the stability of the atoms that form it.
There are 3 types of bonds. They are formed when electrons are shared between two atoms. Key Concepts and Summary.
Covalent bonding occurs when an electron from each of the bonding atoms is donated to an electron pair. We know that a covalent bond involves the sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms - but how does this happen and how does it lead to the formation of a bond holding. Valence bond theory describes bonding as a consequence of the overlap of two separate atomic orbitals on different atoms that creates a region with one pair.
For example carbon has four valence electrons and because of the octet. When Carbon TetraChloride is formed Carbon which has an electron configuration of of. Valence bond theory describes a covalent bond as the overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals each containing a single electron that yield a pair of electrons shared between the two bonded.
Ionic bonds are formed through the exchange of valence electrons between atoms typically a metal and a nonmetal. Each of these orbitals can accept a. A covalent bond is formed by equal sharing of electrons from both the participating atoms.
Covalent bonds occur when atoms share pairs of electrons. Nonmetals will readily form covalent bonds with other. Electrons in the outer shells that are not filled are called valence electrons.
The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called shared. The 3d x 2-y 2 3d z 2 4s 4p x 4p y and 4p z orbitals are then mixed to form a set of empty d 2 sp 3 orbitals that point toward the corners of an octahedron. As the atoms collide with each other some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the surroundings.

Covalent Bond Definition Types And Examples
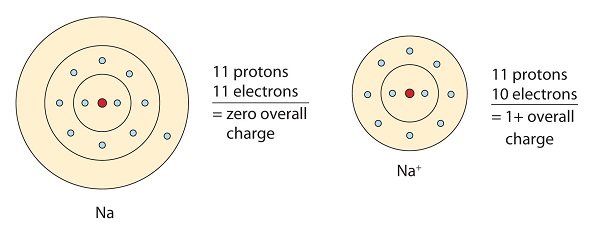
1 3 Ionic And Covalent Bonds Chemistry Libretexts
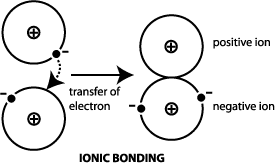
Comments
Post a Comment